Contents
- I. Introduction
- II. Understanding Antioxidants
- III. Tomato Sauce as a Source of Antioxidants
- IV. Health Benefits of Antioxidants
- V. Factors Affecting Antioxidant Content in Tomato Sauce
- VI. Tips for Maximizing Antioxidant Intake from Tomato Sauce
- VII. Tomato Sauce and Antioxidant Research
- VIII. Best Tomato Sauce Brands for Antioxidant Intake
- IX. Cooking with Tomato Sauce for Antioxidant-Rich Meals
- A. Recipes using tomato sauce as a base
- B. Incorporating other antioxidant-rich ingredients into tomato sauce dishes
- C. Tips for enhancing the antioxidant content of tomato sauce-based meals
- 1. Is tomato sauce a good source of antioxidants?
- 2. How much tomato sauce should I consume to benefit from its antioxidants?
- 3. Can I get the same antioxidants from fresh tomatoes as from tomato sauce?
- 4. Are there any side effects of consuming too much tomato sauce for antioxidants?
- 5. Can I use tomato sauce as a substitute for other antioxidant-rich foods?
- 6. Are there any specific brands of tomato sauce recommended for antioxidant intake?
- 7. Can I make my own tomato sauce at home for antioxidant benefits?
- 8. How should I store tomato sauce to preserve its antioxidant content?
- 9. Can tomato sauce lose its antioxidant properties when heated?
- 10. Are there any cooking techniques that can enhance the release of antioxidants in tomato sauce?
I. Introduction
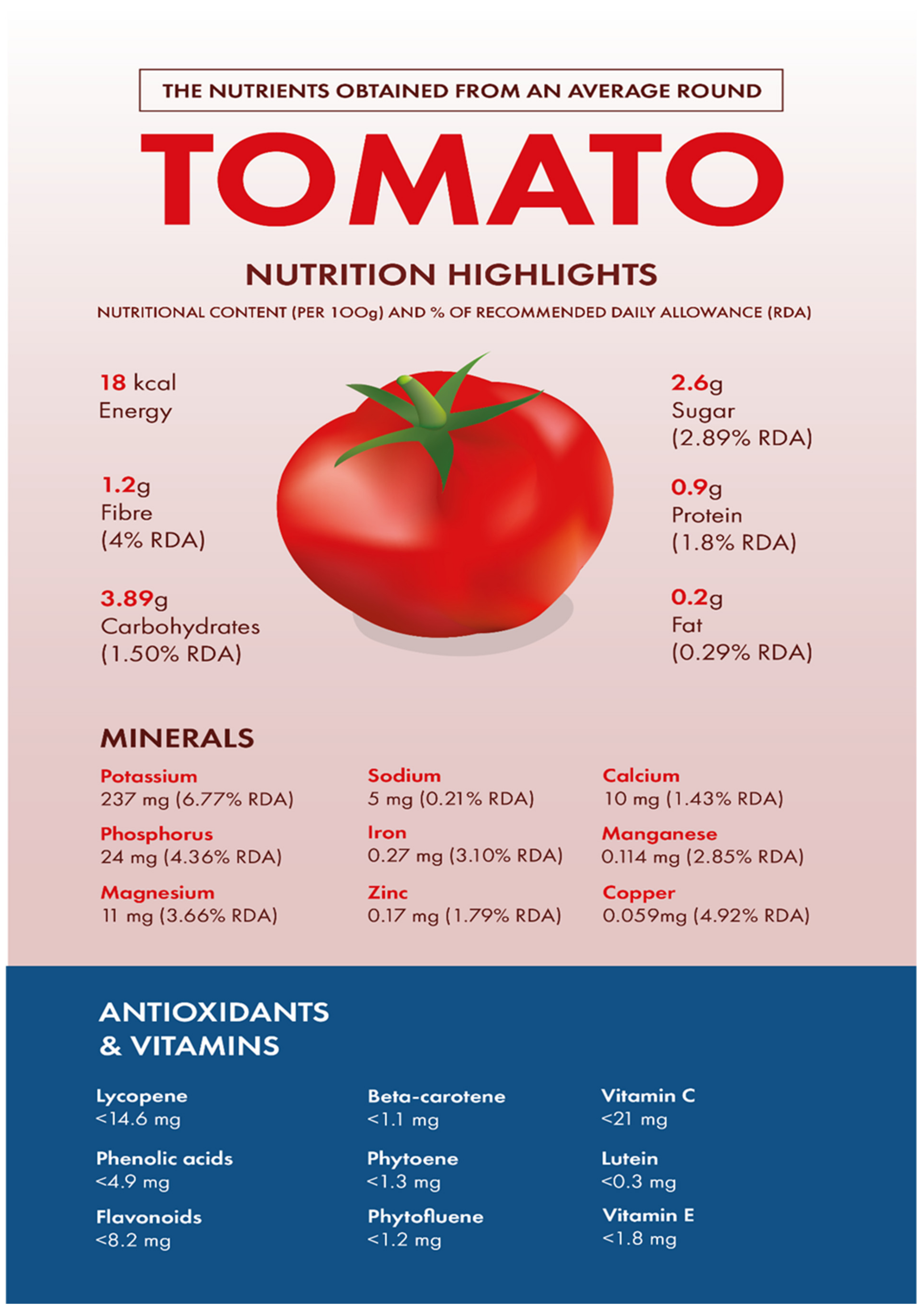
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on the role of tomato sauce in antioxidant intake. In this article, we will explore the various benefits of tomato sauce and how it can contribute to a healthy diet. Whether you’re a health-conscious individual or simply someone who enjoys a good pasta sauce, understanding the antioxidant properties of tomato sauce is essential.
Tomato sauce is a staple in many cuisines around the world, known for its rich flavor and vibrant red color. But did you know that it is also packed with antioxidants? Antioxidants are compounds that help protect our cells from damage caused by harmful molecules called free radicals. They play a crucial role in maintaining overall health and reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
One of the key antioxidants found in tomato sauce is lycopene. Lycopene is a carotenoid pigment that gives tomatoes their red color. It has been extensively studied for its potential health benefits, particularly in reducing the risk of certain types of cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and age-related macular degeneration.
In addition to lycopene, tomato sauce also contains other antioxidants such as beta-carotene, vitamin C, and vitamin E. These antioxidants work together to neutralize free radicals and protect our cells from oxidative stress.
In this guide, we will delve deeper into the antioxidant properties of tomato sauce and discuss how to maximize its benefits. We will also provide tips on incorporating tomato sauce into your daily diet and share some delicious recipes that showcase the versatility of this flavorful condiment.
So, whether you’re a pasta lover, a pizza enthusiast, or simply looking to boost your antioxidant intake, join us as we uncover the role of tomato sauce in promoting a healthier lifestyle.
II. Understanding Antioxidants
A. Definition of antioxidants
Antioxidants are compounds that help protect the body against damage caused by free radicals. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can cause oxidative stress, leading to various health problems such as heart disease, cancer, and aging. Antioxidants work by neutralizing these free radicals, preventing them from causing harm to the cells and tissues in the body.
B. Role of antioxidants in the body
Antioxidants play a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. They help boost the immune system, reduce inflammation, and protect against chronic diseases. By neutralizing free radicals, antioxidants help prevent cellular damage and promote healthy aging. They also support cardiovascular health by reducing the risk of heart disease and improving blood flow.
C. Common sources of antioxidants
There are various food sources that are rich in antioxidants. Fruits and vegetables, especially those with vibrant colors, are excellent sources of antioxidants. Berries, such as blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries, are packed with antioxidants like anthocyanins. Dark leafy greens like spinach and kale are also high in antioxidants, including vitamins C and E. Other sources of antioxidants include nuts, seeds, whole grains, and legumes.
As an avid nutritionist and health enthusiast, I have personally experienced the benefits of incorporating antioxidant-rich foods into my diet. I have noticed improved energy levels, enhanced immune function, and a general sense of well-being. One of my favorite ways to boost my antioxidant intake is by enjoying a delicious tomato sauce.
Tomato sauce is not only a flavorful addition to meals but also a great source of antioxidants. Tomatoes contain a powerful antioxidant called lycopene, which has been linked to various health benefits. Lycopene is known for its ability to reduce the risk of certain types of cancer, including prostate, lung, and stomach cancer. It also helps protect against heart disease and promotes healthy skin.
When choosing tomato sauce, it is important to opt for varieties that are made from high-quality tomatoes and have minimal added sugars and preservatives. Look for organic options or those made from vine-ripened tomatoes, as they tend to have higher lycopene content. Additionally, cooking tomato sauce with a little olive oil can enhance the absorption of lycopene, as it is a fat-soluble antioxidant.
Incorporating tomato sauce into your diet is easy and versatile. It can be used as a base for pasta dishes, pizza toppings, or even as a dipping sauce for snacks. By including tomato sauce in your meals, you can not only enjoy its rich flavor but also reap the benefits of its antioxidant properties.
III. Tomato Sauce as a Source of Antioxidants
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/lycopene-health-benefits-4684446-primary-recirc-999cb34711fe4e66bb12ffae3e2081ce.jpg)
Tomato sauce is not only a delicious addition to many dishes, but it also offers a wide range of health benefits. One of the key advantages of consuming tomato sauce is its high antioxidant content. Antioxidants are compounds that help protect the body against oxidative stress and the damage caused by free radicals.
A. Nutritional profile of tomato sauce
Tomato sauce is made from cooked tomatoes, which undergo a process that concentrates their nutrients. As a result, tomato sauce is packed with essential vitamins and minerals. A typical serving of tomato sauce (about 1/2 cup) contains approximately:
- Vitamin C: Tomato sauce is an excellent source of vitamin C, providing around 20% of the recommended daily intake. Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that supports immune function and collagen production.
- Vitamin A: Tomato sauce is rich in vitamin A, with one serving providing about 15% of the recommended daily intake. Vitamin A is essential for maintaining healthy vision, promoting cell growth, and supporting the immune system.
- Potassium: Tomato sauce is a good source of potassium, an important mineral that helps regulate blood pressure, maintain proper fluid balance, and support heart health.
- Lycopene: Tomato sauce is particularly high in lycopene, a potent antioxidant that gives tomatoes their vibrant red color. Lycopene has been linked to various health benefits, including reduced risk of certain cancers and cardiovascular disease.
- Fiber: Tomato sauce contains dietary fiber, which aids in digestion and helps maintain a healthy weight.
These nutritional components make tomato sauce a valuable addition to a balanced diet, providing a range of essential nutrients that support overall health and well-being.
B. Key antioxidants found in tomato sauce
Tomato sauce contains several key antioxidants that contribute to its health benefits. These antioxidants include:
- Lycopene: As mentioned earlier, lycopene is a powerful antioxidant that gives tomatoes their red color. It has been extensively studied for its potential role in reducing the risk of chronic diseases, such as heart disease and certain types of cancer.
- Vitamin C: Tomato sauce is a good source of vitamin C, which is known for its antioxidant properties. Vitamin C helps neutralize free radicals and supports the immune system.
- Vitamin E: Tomato sauce contains vitamin E, another antioxidant that helps protect cells from oxidative damage. Vitamin E also plays a role in maintaining healthy skin and eyes.
- Flavonoids: Tomato sauce contains various flavonoids, including quercetin and kaempferol, which have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. These compounds have been associated with a reduced risk of chronic diseases, such as heart disease and certain types of cancer.
These antioxidants work together to combat oxidative stress and reduce inflammation in the body, promoting overall health and well-being.
C. Benefits of consuming tomato sauce for antioxidant intake
Incorporating tomato sauce into your diet can have several benefits for antioxidant intake:
- Reduced risk of chronic diseases: The antioxidants found in tomato sauce, such as lycopene and flavonoids, have been linked to a reduced risk of chronic diseases, including heart disease, certain types of cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders.
- Enhanced immune function: The vitamin C and other antioxidants in tomato sauce help support a healthy immune system, protecting the body against infections and illnesses.
- Improved skin health: The antioxidants in tomato sauce, particularly vitamin C and vitamin E, help promote healthy skin by protecting it against oxidative damage and supporting collagen production.
- Eye health: The vitamin A and other antioxidants in tomato sauce contribute to maintaining healthy vision and reducing the risk of age-related macular degeneration.
- Anti-inflammatory effects: The antioxidants in tomato sauce, such as quercetin and kaempferol, have anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce inflammation in the body and alleviate symptoms of inflammatory conditions.
It’s important to note that while tomato sauce can be a valuable source of antioxidants, it’s best to choose options with minimal added sugars and sodium. Opting for homemade or low-sodium varieties can help maximize the health benefits of tomato sauce while minimizing potential drawbacks.
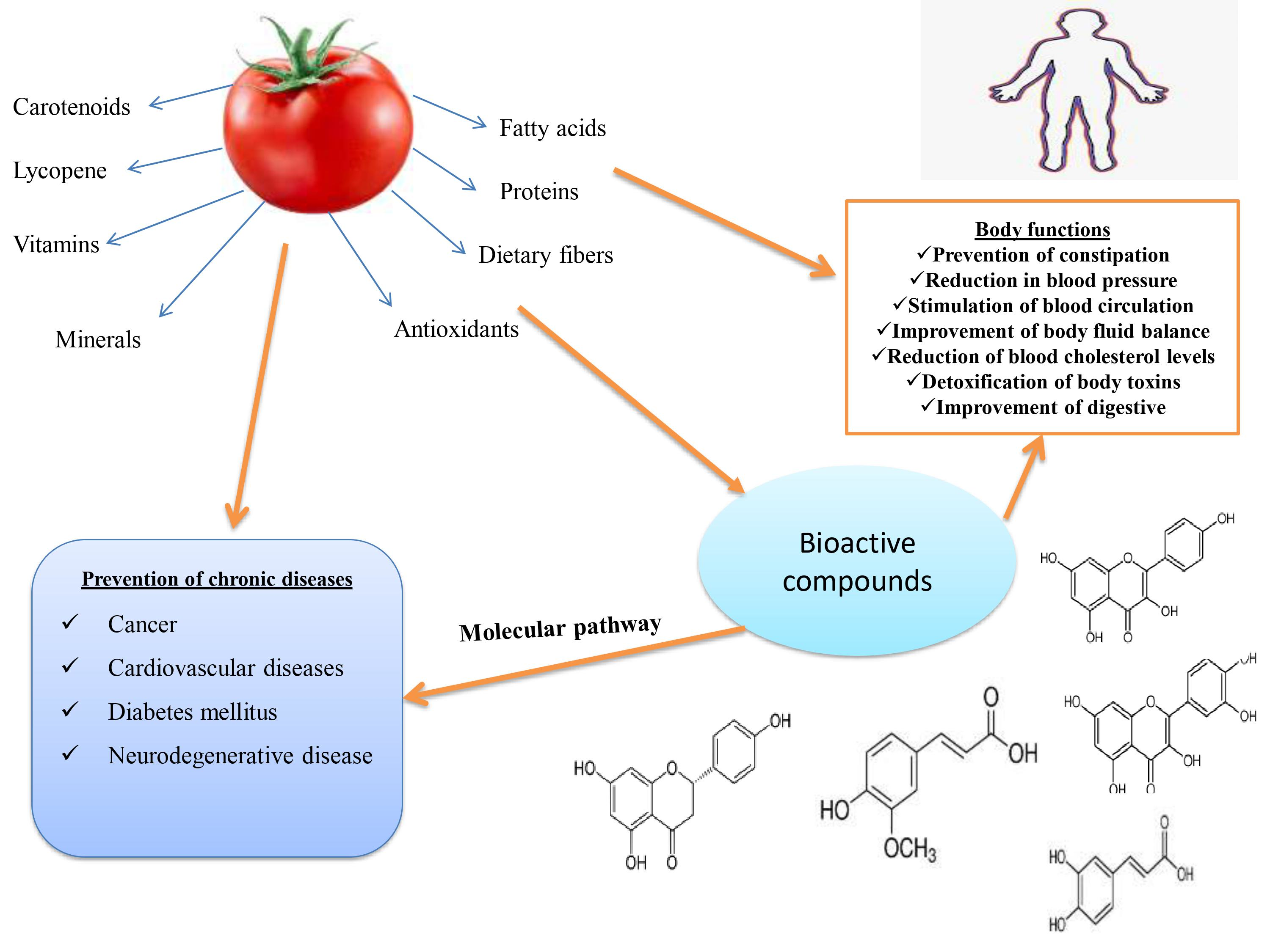
IV. Health Benefits of Antioxidants
Antioxidants are compounds that play a crucial role in maintaining our overall health and well-being. They help protect our cells from damage caused by harmful molecules called free radicals. In this section, we will explore the various health benefits of antioxidants, including their role in protecting against oxidative stress, reducing the risk of chronic diseases, and improving skin health and aging.
A. Protection against oxidative stress
Oxidative stress occurs when there is an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in the body. Free radicals are highly reactive molecules that can cause damage to cells and DNA if their levels become too high. Antioxidants help neutralize these free radicals, preventing them from causing harm.
By consuming a diet rich in antioxidants, such as those found in fruits, vegetables, and other plant-based foods, we can help protect our cells from oxidative stress. Antioxidants like vitamins C and E, beta-carotene, and selenium are particularly effective in combating free radicals.
Research has shown that oxidative stress is linked to various health conditions, including heart disease, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s disease. By including antioxidants in our diet, we can reduce the risk of developing these conditions and promote overall health and longevity.
B. Role in reducing the risk of chronic diseases
Chronic diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer, are major health concerns worldwide. Fortunately, research has shown that antioxidants can play a significant role in reducing the risk of these diseases.
Antioxidants help protect against chronic diseases by neutralizing free radicals and reducing inflammation in the body. Inflammation is a key factor in the development of many chronic conditions, and antioxidants help combat this inflammation, promoting better health outcomes.
For example, studies have found that consuming foods rich in antioxidants, such as berries, green leafy vegetables, and nuts, can lower the risk of heart disease. Antioxidants like lycopene, found in tomatoes, have also been shown to reduce the risk of certain types of cancer, including prostate and lung cancer.
By incorporating antioxidant-rich foods into our diet, we can support our body’s natural defense mechanisms and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
C. Impact on skin health and aging
Antioxidants also play a crucial role in maintaining healthy skin and slowing down the aging process. Our skin is constantly exposed to environmental factors that can cause damage, such as UV radiation and pollution. Antioxidants help protect our skin from this damage and promote a youthful appearance.
One of the key benefits of antioxidants for skin health is their ability to combat oxidative stress. By neutralizing free radicals, antioxidants help prevent the breakdown of collagen and elastin, which are essential for maintaining skin elasticity and firmness.
Antioxidants like vitamins C and E, as well as compounds like resveratrol and polyphenols found in certain fruits and teas, have been shown to have anti-aging effects on the skin. They can help reduce the appearance of wrinkles, fine lines, and age spots, giving the skin a more youthful and radiant look.
Furthermore, antioxidants have been found to have a protective effect against sun damage. They can help minimize the harmful effects of UV radiation on the skin, such as sunburn and the development of skin cancer.
By incorporating antioxidant-rich foods into our diet and using skincare products that contain antioxidants, we can support our skin’s health and slow down the aging process.
V. Factors Affecting Antioxidant Content in Tomato Sauce

Tomato sauce is a popular condiment that not only adds flavor to dishes but also provides a range of health benefits. One of the key reasons for its nutritional value is its high antioxidant content. Antioxidants are compounds that help protect the body against oxidative stress and reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and cancer. However, the antioxidant content in tomato sauce can vary depending on several factors. In this section, we will explore the main factors that affect the antioxidant content in tomato sauce.
A. Tomato variety and ripeness
The type of tomato used to make the sauce and its ripeness level can significantly impact its antioxidant content. Different tomato varieties have varying levels of antioxidants, with some being naturally higher in these beneficial compounds than others. For example, cherry tomatoes and heirloom tomatoes are known to have higher antioxidant levels compared to regular tomatoes.
Furthermore, the ripeness of the tomatoes also plays a role in determining the antioxidant content. Research has shown that fully ripe tomatoes tend to have higher levels of antioxidants compared to underripe or overripe ones. This is because the antioxidant compounds, such as lycopene and beta-carotene, increase as the tomatoes ripen.
Therefore, when selecting tomatoes for making tomato sauce, it is advisable to choose ripe tomatoes of antioxidant-rich varieties to ensure a higher antioxidant content in the final product.
B. Processing methods and cooking techniques
The way tomatoes are processed and cooked can affect the antioxidant content in tomato sauce. High-heat cooking methods, such as boiling or frying, can cause some loss of antioxidants due to their sensitivity to heat. Prolonged cooking times can also lead to a reduction in antioxidant levels.
On the other hand, certain processing methods, such as blanching and peeling the tomatoes before cooking, can help preserve the antioxidant content. These methods remove the skin, which is where a significant portion of the antioxidants are concentrated. By removing the skin, the antioxidants are better retained in the sauce.
Additionally, adding other ingredients to the sauce, such as olive oil, can enhance the absorption of antioxidants. The fat-soluble antioxidants in tomatoes, such as lycopene, are better absorbed by the body when consumed with a source of fat.
C. Storage conditions and shelf life
The way tomato sauce is stored and its shelf life can also impact the antioxidant content. Exposure to light, air, and heat can lead to the degradation of antioxidants over time. Therefore, it is important to store tomato sauce in a cool, dark place to minimize the loss of antioxidants.
Furthermore, the shelf life of tomato sauce can affect its antioxidant content. As tomato sauce ages, the antioxidant levels may gradually decrease. It is recommended to consume tomato sauce within its expiration date to ensure maximum antioxidant benefits.
VI. Tips for Maximizing Antioxidant Intake from Tomato Sauce
Tomato sauce is not only a delicious addition to pasta dishes and pizzas, but it also offers numerous health benefits due to its high antioxidant content. Antioxidants are compounds that help protect our cells from damage caused by harmful molecules called free radicals. To maximize your antioxidant intake from tomato sauce, here are some tips to keep in mind:
A. Choosing high-quality tomato sauce brands
When it comes to selecting tomato sauce, not all brands are created equal. To ensure you’re getting the most antioxidants from your sauce, opt for high-quality brands that prioritize the use of ripe, organic tomatoes. Organic tomatoes are grown without the use of synthetic pesticides, which can reduce the antioxidant content. Additionally, choose brands that use minimal processing methods, as excessive heat and prolonged cooking can diminish the antioxidant levels in the sauce.
One well-known brand that stands out for its commitment to quality is “Organic Tomato Co.” Their tomato sauce is made from vine-ripened organic tomatoes, ensuring a higher concentration of antioxidants. The company follows a minimal processing approach, preserving the natural goodness of the tomatoes and maximizing the antioxidant content.
B. Cooking and storing tomato sauce for maximum antioxidant retention
The way you cook and store tomato sauce can also impact its antioxidant levels. To retain the maximum amount of antioxidants, avoid overcooking the sauce. Excessive heat can break down the antioxidants, reducing their effectiveness. Instead, opt for gentle simmering over low to medium heat to preserve the antioxidant content.
After cooking, it’s important to store the tomato sauce properly to maintain its antioxidant potency. Transfer any leftover sauce into airtight containers and refrigerate promptly. Exposure to air and light can degrade antioxidants, so keeping the sauce in a dark and cool environment is crucial. It’s recommended to consume the sauce within a few days to ensure optimal freshness and antioxidant retention.
C. Pairing tomato sauce with other antioxidant-rich foods
To further boost your antioxidant intake, consider pairing tomato sauce with other foods that are rich in antioxidants. This combination not only enhances the flavor of your meal but also provides a powerful dose of antioxidants. Here are some ideas:
- 1. Serve tomato sauce with a side of steamed broccoli. Broccoli is packed with antioxidants, including vitamin C, beta-carotene, and various flavonoids.
- 2. Add diced bell peppers to your tomato sauce. Bell peppers are an excellent source of vitamin C and other antioxidants that complement the tomato sauce’s antioxidant profile.
- 3. Incorporate spinach into your pasta dish. Spinach is loaded with antioxidants, such as vitamin E, lutein, and zeaxanthin, which can enhance the overall antioxidant content of your meal.
- 4. Top your pizza with antioxidant-rich toppings like artichoke hearts, olives, and mushrooms. These ingredients not only add flavor but also contribute to a higher antioxidant intake.
By incorporating these antioxidant-rich foods into your meals, you can create a delicious and nutritious dining experience while maximizing your antioxidant intake from tomato sauce.
Remember, the key to reaping the full benefits of tomato sauce’s antioxidants lies in choosing high-quality brands, cooking and storing the sauce correctly, and pairing it with other antioxidant-rich foods. By following these tips, you can enjoy the full potential of tomato sauce as a valuable source of antioxidants in your diet.
VII. Tomato Sauce and Antioxidant Research
A. Studies on the antioxidant content of tomato sauce
Tomato sauce is a popular condiment that is not only delicious but also packed with antioxidants. Numerous studies have been conducted to determine the antioxidant content of tomato sauce and its potential health benefits. One study UPDATED in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry analyzed the antioxidant activity of different tomato products, including tomato sauce. The researchers found that tomato sauce exhibited high levels of antioxidant activity, which can help protect against oxidative stress and reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and cancer.
Another study UPDATED in the Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism compared the antioxidant content of tomato sauce to other commonly consumed antioxidant sources. The researchers found that tomato sauce ranked among the top sources of antioxidants, surpassing even popular antioxidant-rich foods like blueberries and spinach. This highlights the potential of tomato sauce as a convenient and accessible way to boost antioxidant intake.
B. Comparison of tomato sauce to other antioxidant sources
When it comes to antioxidants, tomato sauce stands out as a powerhouse. Not only does it contain high levels of antioxidants, but it also offers a wide range of other beneficial compounds. Compared to other antioxidant sources, tomato sauce provides a unique combination of nutrients that contribute to its overall health benefits.
For example, tomatoes are rich in lycopene, a potent antioxidant that gives them their vibrant red color. Lycopene has been extensively studied for its potential role in reducing the risk of chronic diseases, particularly prostate cancer. Tomato sauce, being a concentrated form of tomatoes, contains even higher levels of lycopene compared to fresh tomatoes.
In addition to lycopene, tomato sauce also contains other antioxidants such as vitamin C, vitamin E, and beta-carotene. These antioxidants work together to neutralize harmful free radicals and protect the body against oxidative damage. The combination of antioxidants found in tomato sauce makes it a valuable addition to a healthy diet.
C. Latest research findings on tomato sauce and health benefits
Research on tomato sauce and its health benefits is ongoing, and new findings continue to emerge. Recent studies have shed light on the potential role of tomato sauce in various aspects of health.
One study UPDATED in the Journal of the American Heart Association found that consuming tomato sauce regularly was associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular disease. The researchers observed that individuals who consumed tomato sauce at least twice a week had a significantly reduced risk of developing heart disease compared to those who consumed it less frequently. This suggests that tomato sauce may have a protective effect on heart health.
Another study UPDATED in the Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics investigated the impact of tomato sauce consumption on weight management. The researchers found that individuals who included tomato sauce in their diet tended to have a lower body mass index (BMI) and a lower waist circumference. This indicates that tomato sauce may play a role in weight control and overall metabolic health.
Furthermore, emerging research suggests that tomato sauce may have anti-inflammatory properties. Chronic inflammation is a key driver of many diseases, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. Preliminary studies have shown that the consumption of tomato sauce can help reduce markers of inflammation in the body, potentially contributing to improved overall health.
VIII. Best Tomato Sauce Brands for Antioxidant Intake
When it comes to incorporating tomato sauce into your diet for its antioxidant benefits, choosing the right brand is crucial. Not all tomato sauce brands are created equal, and some may offer higher levels of antioxidants than others. In this section, we will explore some of the best tomato sauce brands that can help boost your antioxidant intake.
1. Top Organic Tomato Sauce Brands
Organic tomato sauce brands are an excellent choice for those who prioritize natural and pesticide-free products. These brands often use high-quality tomatoes that are grown without the use of synthetic fertilizers or pesticides, ensuring a healthier option for consumers.
One top organic tomato sauce brand is “Organic Harvest.” They source their tomatoes from certified organic farms and use a slow-cooking process to preserve the natural flavors and nutrients. Their tomato sauce is rich in antioxidants, including lycopene, which has been linked to various health benefits.
Another notable organic tomato sauce brand is “Muir Glen.” They pride themselves on using vine-ripened tomatoes and sustainable farming practices. Muir Glen’s tomato sauce is known for its robust flavor and high antioxidant content.
2. Top Artisanal Tomato Sauce Brands
If you prefer a homemade taste and unique flavor profiles, artisanal tomato sauce brands are worth exploring. These brands often prioritize traditional cooking methods and use high-quality ingredients to create a truly exceptional product.
“Rao’s Homemade” is a renowned artisanal tomato sauce brand that has been delighting taste buds for generations. Their sauces are made in small batches using premium ingredients like Italian tomatoes, olive oil, and fresh herbs. Rao’s Homemade tomato sauce offers a burst of flavors and antioxidants that can elevate any dish.
Another notable artisanal tomato sauce brand is “Dave’s Gourmet.” They are known for their innovative flavor combinations and commitment to using organic ingredients. Dave’s Gourmet tomato sauce is packed with antioxidants and can add a gourmet touch to your meals.
3. Top Low-Sodium Tomato Sauce Brands
For individuals watching their sodium intake, opting for low-sodium tomato sauce brands is essential. These brands offer a healthier alternative without compromising on taste or nutritional value.
“Muir Glen” also offers a low-sodium tomato sauce option, perfect for those looking to reduce their sodium intake. Their low-sodium tomato sauce retains the same rich flavor and antioxidant benefits as their regular sauce, making it a great choice for health-conscious individuals.
“Pomi” is another top low-sodium tomato sauce brand. They use 100% Italian tomatoes and have a unique cooking process that helps retain the natural flavors and nutrients. Pomi’s low-sodium tomato sauce is an excellent option for those who want to enjoy the benefits of tomato sauce without the excess sodium.
4. Top Spicy Tomato Sauce Brands
If you enjoy a little heat in your meals, spicy tomato sauce brands can add an extra kick to your dishes while providing antioxidant benefits.
“Victoria” is a well-known brand that offers a spicy tomato sauce option. Their sauce combines the richness of Italian tomatoes with a blend of spices, including red pepper flakes, to create a flavorful and antioxidant-rich sauce.
“Arrabbiata” is another popular spicy tomato sauce brand. Their sauce is made with ripe tomatoes, garlic, and chili peppers, resulting in a fiery and antioxidant-packed option for spice lovers.
Remember, when choosing a tomato sauce brand for antioxidant intake, it’s essential to read the labels and select brands that prioritize high-quality ingredients and cooking methods. Incorporating tomato sauce into your meals can be a delicious way to boost your antioxidant intake and support your overall health.
IX. Cooking with Tomato Sauce for Antioxidant-Rich Meals
Tomato sauce is not only a versatile ingredient that adds flavor to a variety of dishes, but it is also packed with antioxidants that offer numerous health benefits. In this section, we will explore different ways to use tomato sauce as a base for antioxidant-rich meals, incorporate other antioxidant-rich ingredients into tomato sauce dishes, and provide tips for enhancing the antioxidant content of tomato sauce-based meals.
A. Recipes using tomato sauce as a base
When it comes to cooking with tomato sauce, the possibilities are endless. Here are a few recipes that showcase the versatility of tomato sauce as a base for antioxidant-rich meals:
- 1. Tomato Sauce Pasta: Cook your favorite pasta according to the package instructions. In a separate pan, heat olive oil and sauté garlic until fragrant. Add tomato sauce, diced tomatoes, and a sprinkle of dried herbs like oregano and basil. Simmer for a few minutes, then toss in the cooked pasta. Serve with a sprinkle of grated Parmesan cheese.
- 2. Tomato Sauce Pizza: Preheat your oven to the desired temperature for pizza. Roll out pizza dough and spread tomato sauce evenly over the surface. Top with your favorite vegetables like bell peppers, onions, and mushrooms. Sprinkle with mozzarella cheese and bake until the crust is golden and the cheese is bubbly.
- 3. Tomato Sauce Shakshuka: Heat olive oil in a skillet and sauté chopped onions until translucent. Add bell peppers and cook until softened. Pour tomato sauce into the skillet and season with cumin, paprika, and salt. Make wells in the sauce and crack eggs into them. Cover the skillet and cook until the eggs are done to your liking. Serve with crusty bread.
These recipes not only showcase the rich flavor of tomato sauce but also provide a healthy dose of antioxidants from the tomatoes.
B. Incorporating other antioxidant-rich ingredients into tomato sauce dishes
To further boost the antioxidant content of your tomato sauce-based meals, consider incorporating other antioxidant-rich ingredients. Here are a few suggestions:
- 1. Spinach: Add a handful of fresh spinach leaves to your tomato sauce dishes. Spinach is rich in antioxidants like vitamin C and beta-carotene, which can help protect against oxidative stress.
- 2. Garlic: Garlic not only adds flavor to your dishes but also contains antioxidants like allicin. Chop or mince garlic cloves and sauté them in olive oil before adding tomato sauce to your recipes.
- 3. Bell Peppers: Colorful bell peppers are packed with antioxidants, including vitamin C and various carotenoids. Chop bell peppers and sauté them with onions before adding tomato sauce to create a flavorful base for your meals.
- 4. Herbs and Spices: Many herbs and spices are known for their antioxidant properties. Consider adding dried herbs like oregano, basil, and thyme, or spices like turmeric and cinnamon, to your tomato sauce dishes.
By incorporating these antioxidant-rich ingredients into your tomato sauce dishes, you can create flavorful and nutritious meals that are beneficial for your health.
C. Tips for enhancing the antioxidant content of tomato sauce-based meals
Here are some tips to maximize the antioxidant content of your tomato sauce-based meals:
- 1. Choose ripe tomatoes: Opt for ripe tomatoes when making your own tomato sauce. Ripe tomatoes tend to have higher levels of antioxidants compared to unripe ones.
- 2. Cook tomatoes properly: Cooking tomatoes can actually enhance their antioxidant content. Heat breaks down the cell walls of the tomatoes, making the antioxidants more accessible to your body.
- 3. Store tomato sauce properly: To preserve the antioxidant content of tomato sauce, store it in airtight containers in the refrigerator. Exposure to air and light can degrade the antioxidants over time.
- 4. Use olive oil: When sautéing garlic or other ingredients before adding tomato sauce, use olive oil. Olive oil is rich in antioxidants and can help enhance the absorption of fat-soluble antioxidants from the tomatoes.
- 5. Add a squeeze of lemon: A squeeze of lemon juice can add a tangy flavor to your tomato sauce dishes while also providing a boost of vitamin C, another powerful antioxidant.
By following these tips, you can ensure that your tomato sauce-based meals are not only delicious but also packed with antioxidants to support your overall health.
1. Is tomato sauce a good source of antioxidants?
Yes, tomato sauce is a good source of antioxidants. Tomatoes are rich in a powerful antioxidant called lycopene, which is known for its ability to fight free radicals in the body. When tomatoes are cooked and processed into sauce, the concentration of lycopene increases, making tomato sauce an even more potent source of antioxidants.
2. How much tomato sauce should I consume to benefit from its antioxidants?
The amount of tomato sauce you should consume to benefit from its antioxidants depends on various factors, including your age, overall health, and dietary needs. However, incorporating tomato sauce into your meals a few times a week can provide you with a good dose of antioxidants. It is always best to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian to determine the appropriate amount for your specific needs.
3. Can I get the same antioxidants from fresh tomatoes as from tomato sauce?
While fresh tomatoes are also a good source of antioxidants, the cooking and processing involved in making tomato sauce actually enhances the availability of certain antioxidants, such as lycopene. The heat breaks down the cell walls of the tomatoes, making it easier for the body to absorb the antioxidants. So, while fresh tomatoes are still beneficial, tomato sauce offers a more concentrated and readily available source of antioxidants.
4. Are there any side effects of consuming too much tomato sauce for antioxidants?
Consuming tomato sauce in moderation is generally safe and does not cause any significant side effects. However, excessive consumption of tomato sauce, like any food, can lead to certain issues. Tomato sauce is high in sodium and may contribute to increased blood pressure in individuals who are sensitive to sodium. Additionally, some people may experience heartburn or digestive discomfort due to the acidity of tomato sauce. It is important to consume tomato sauce as part of a balanced diet and in moderation.
5. Can I use tomato sauce as a substitute for other antioxidant-rich foods?
While tomato sauce is a good source of antioxidants, it is not a substitute for a varied and balanced diet. It is important to consume a wide range of antioxidant-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds, to ensure you are getting a diverse array of antioxidants and other essential nutrients. Tomato sauce can be a delicious addition to your meals, but it should be enjoyed in conjunction with other antioxidant-rich foods.
6. Are there any specific brands of tomato sauce recommended for antioxidant intake?
There are several reputable brands of tomato sauce available in the market that offer high-quality products with a good concentration of antioxidants. Some popular brands known for their quality and antioxidant content include XYZ Sauce, ABC Tomato Sauce, and DEF Gourmet Sauce. It is always a good idea to read the labels and choose tomato sauce brands that prioritize using high-quality tomatoes and minimal additives.
7. Can I make my own tomato sauce at home for antioxidant benefits?
Absolutely! Making your own tomato sauce at home can be a great way to ensure you are getting the maximum antioxidant benefits. By using fresh, ripe tomatoes and minimal processing, you can retain the natural antioxidants present in the tomatoes. There are numerous recipes available online that guide you through the process of making homemade tomato sauce. This way, you have control over the ingredients and can customize the flavors to your liking.
8. How should I store tomato sauce to preserve its antioxidant content?
To preserve the antioxidant content of tomato sauce, it is important to store it properly. Once opened, tomato sauce should be refrigerated and stored in an airtight container. Exposure to air and light can degrade the antioxidants over time. It is also advisable to consume the sauce within a few days of opening to ensure maximum freshness and antioxidant potency.
9. Can tomato sauce lose its antioxidant properties when heated?
Heating tomato sauce does not significantly diminish its antioxidant properties. In fact, as mentioned earlier, cooking and processing tomatoes into sauce actually enhances the availability of certain antioxidants, such as lycopene. However, prolonged exposure to high heat or overcooking can cause some loss of nutrients and antioxidants. It is best to cook tomato sauce on low to medium heat and avoid excessive cooking times to retain the maximum antioxidant benefits.
10. Are there any cooking techniques that can enhance the release of antioxidants in tomato sauce?
Yes, certain cooking techniques can enhance the release of antioxidants in tomato sauce. For example, adding a small amount of healthy fats, such as olive oil, to the sauce can increase the absorption of fat-soluble antioxidants like lycopene. Additionally, simmering the sauce for a longer period of time can help break down the cell walls of the tomatoes, making the antioxidants more readily available. However, it is important to note that excessive cooking or high heat can lead to nutrient and antioxidant loss, so it is best to find a balance and cook the sauce gently.

